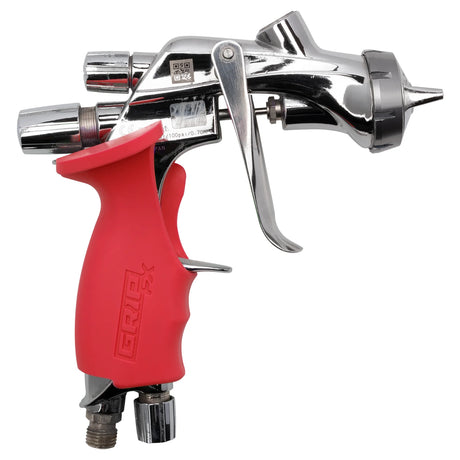
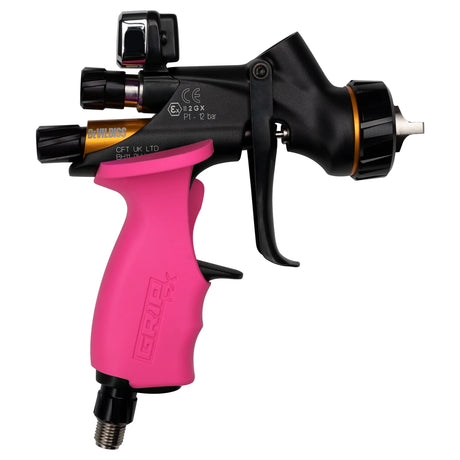
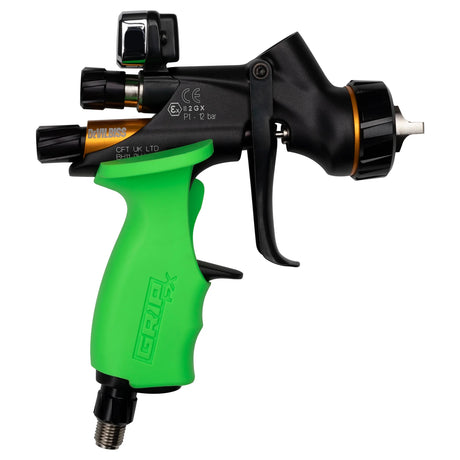
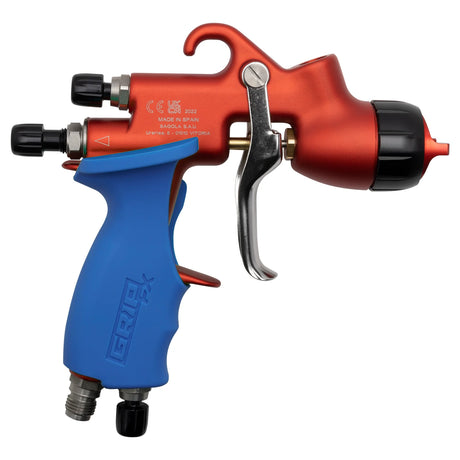
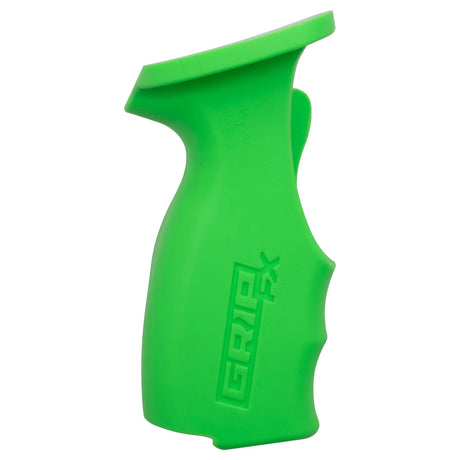
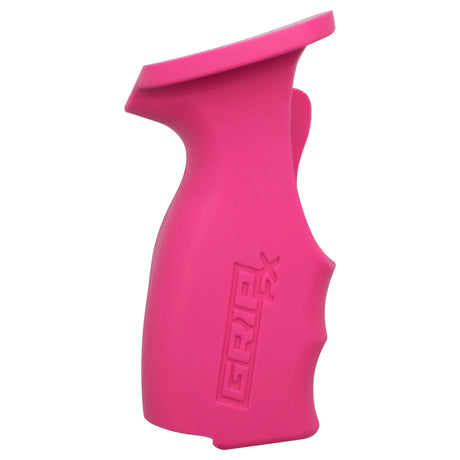
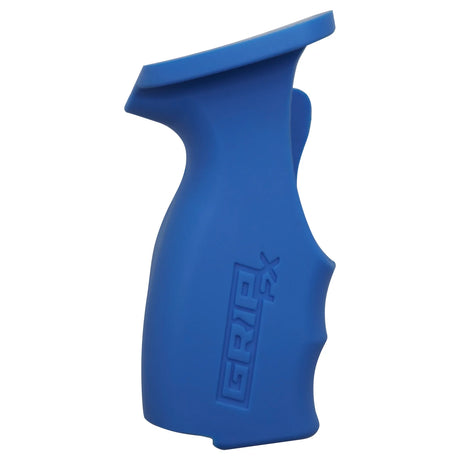
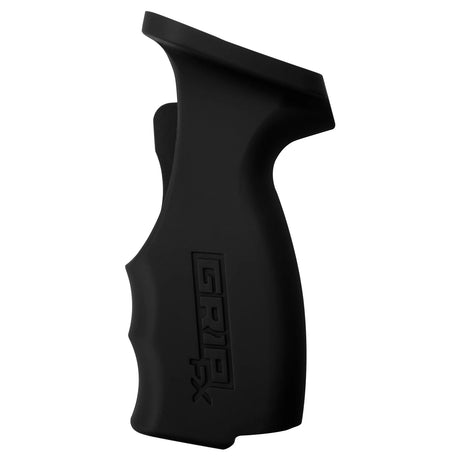
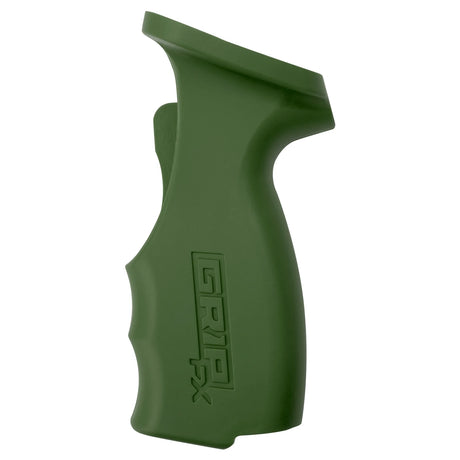
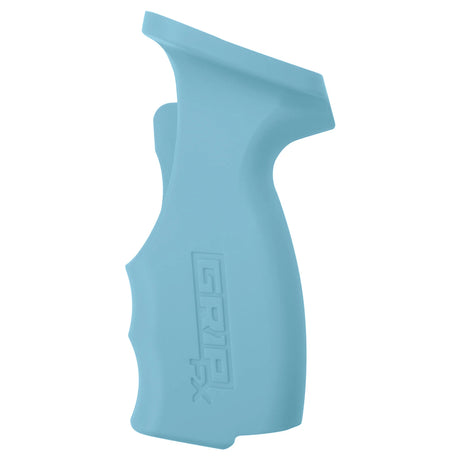
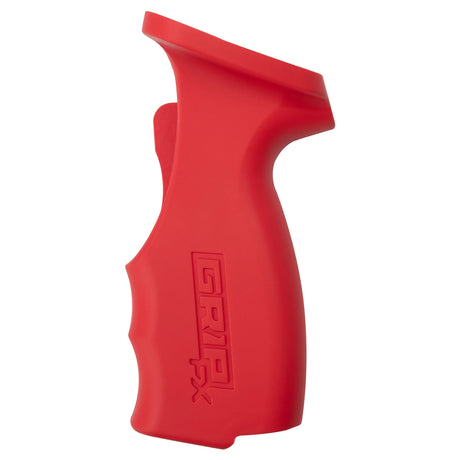
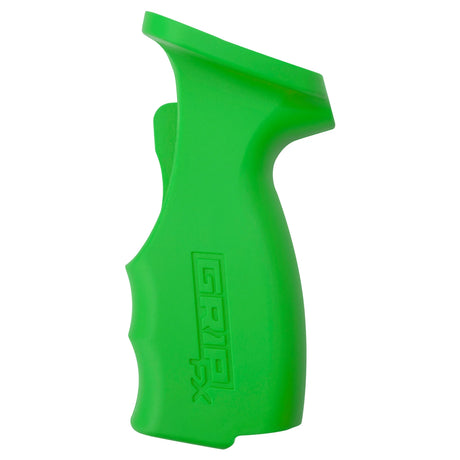
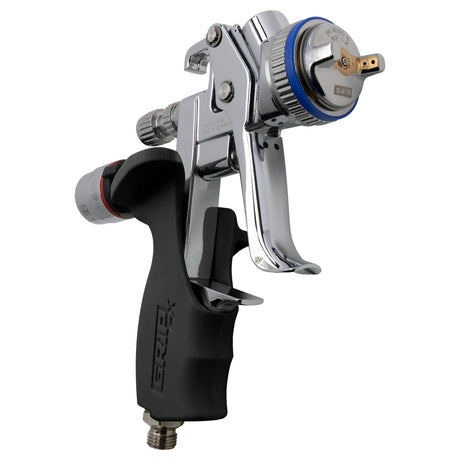
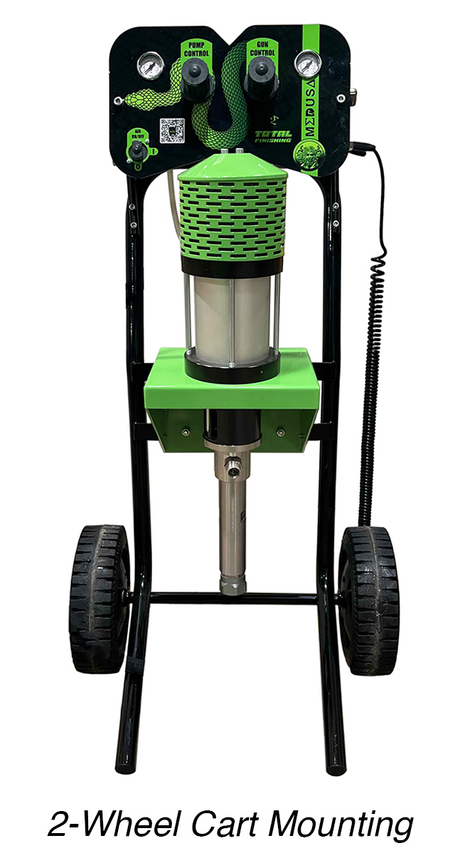
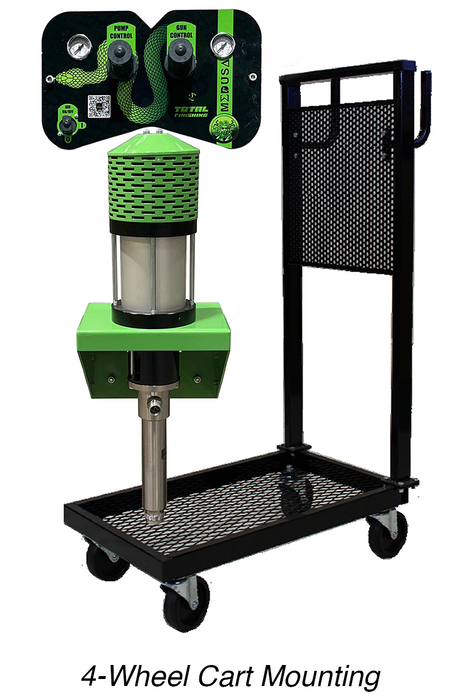
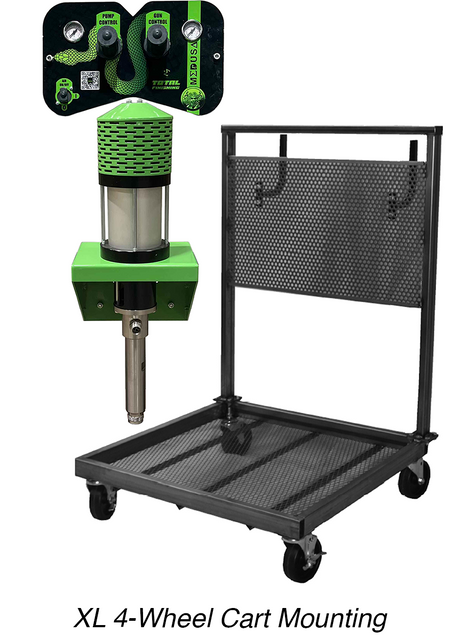
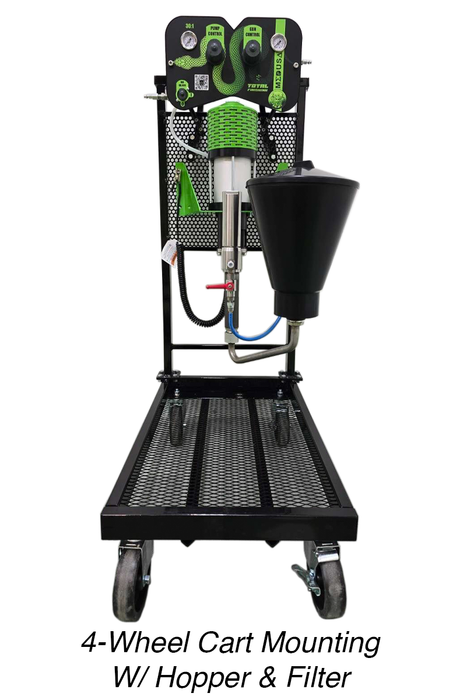
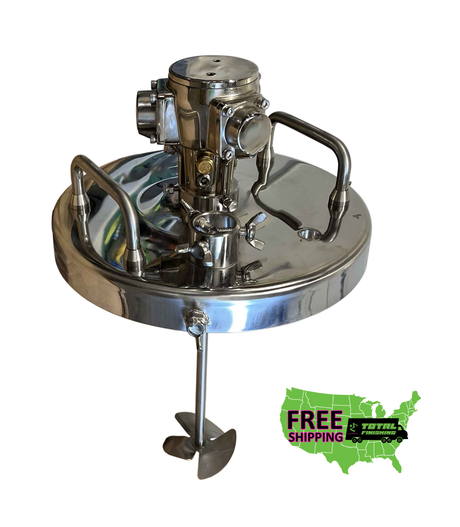
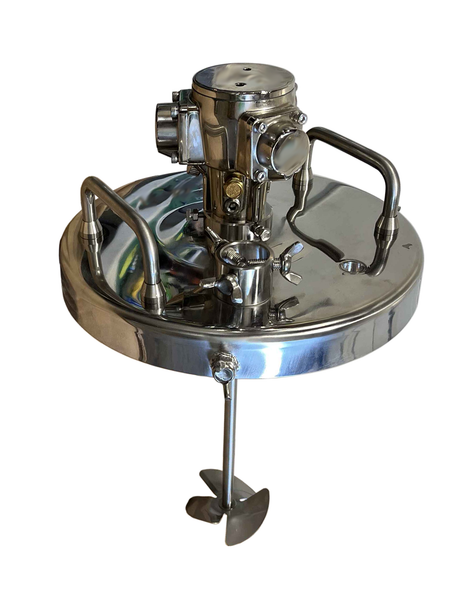
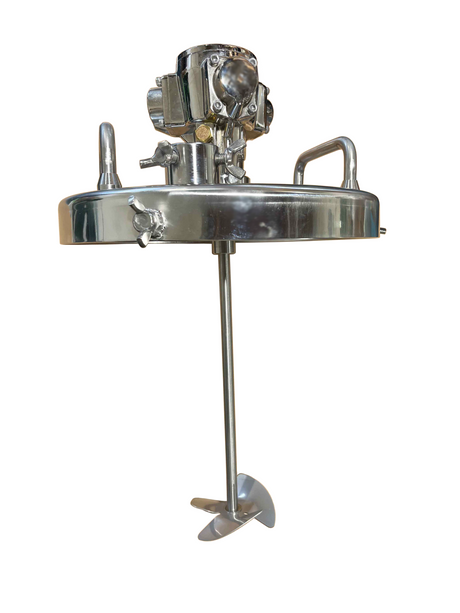
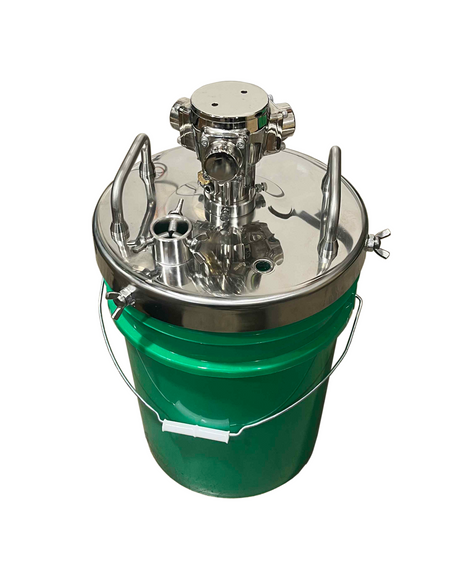
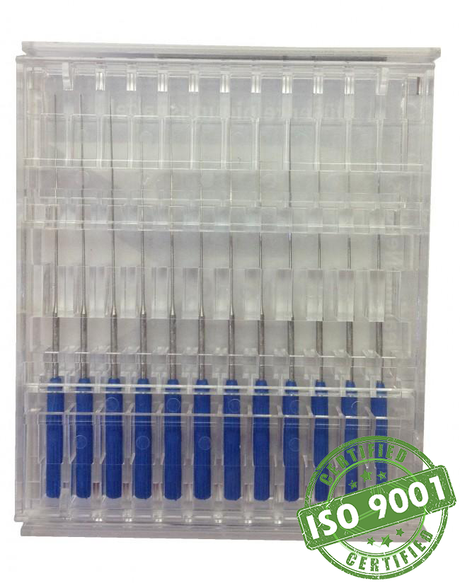
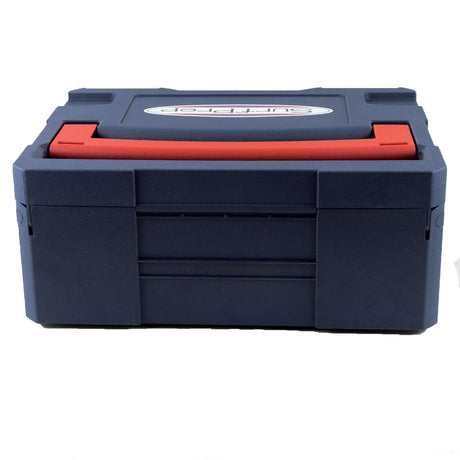
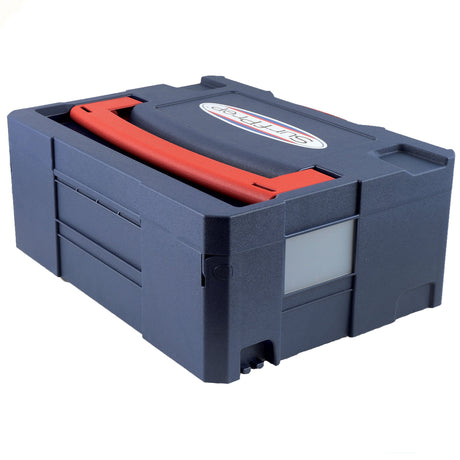
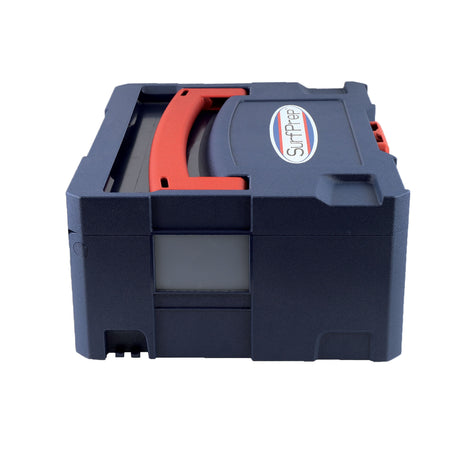
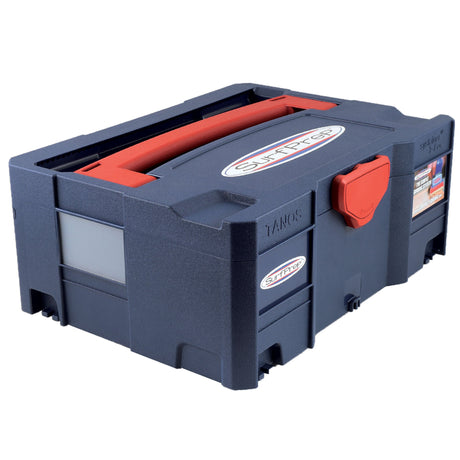
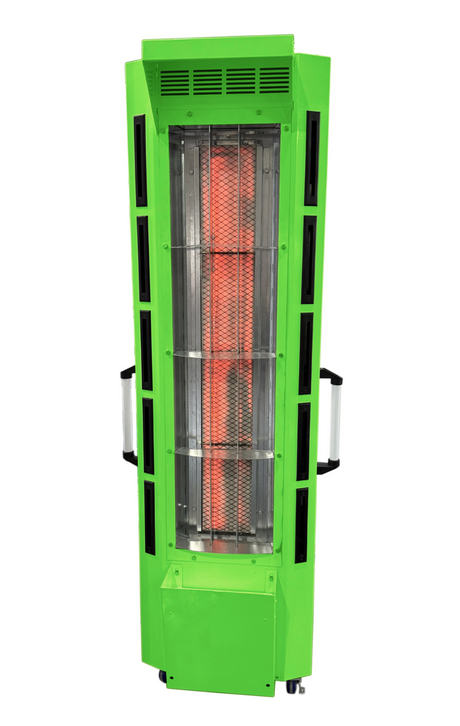
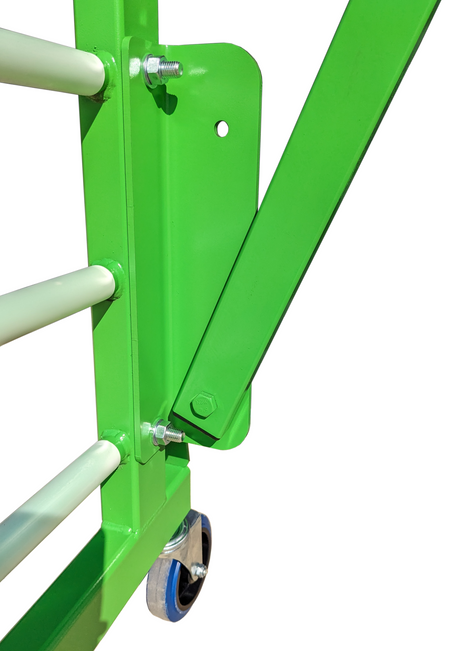
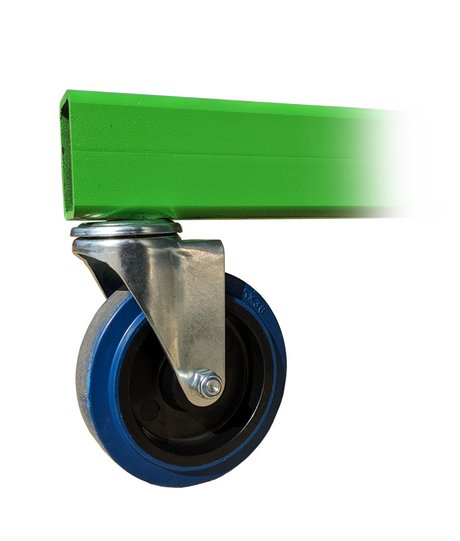
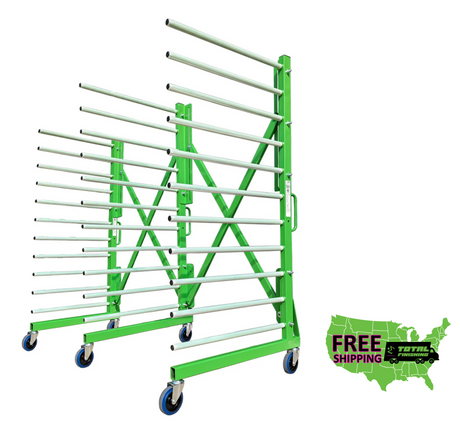
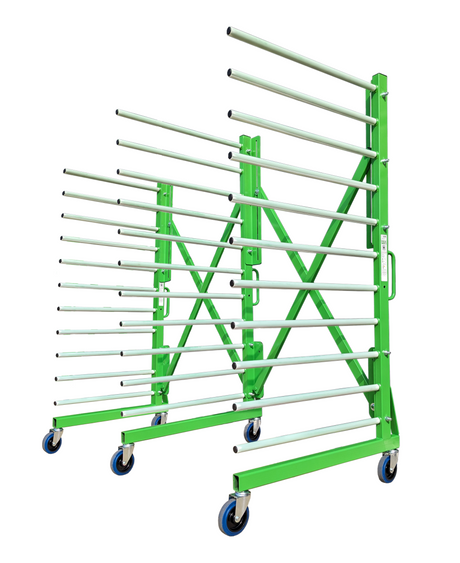
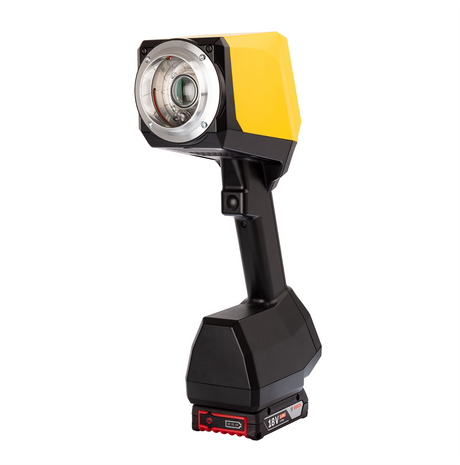
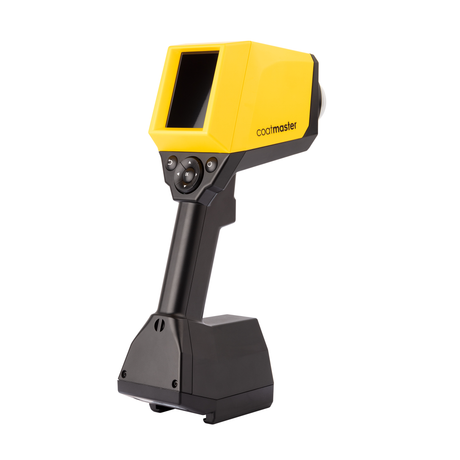
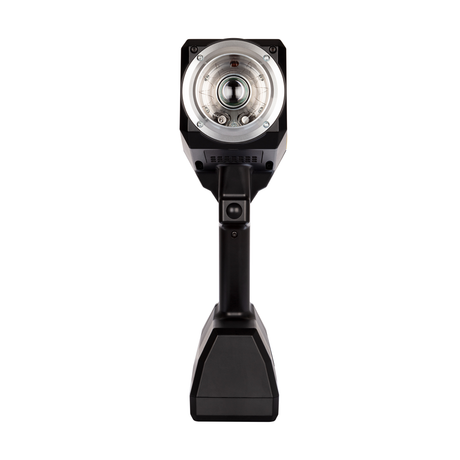
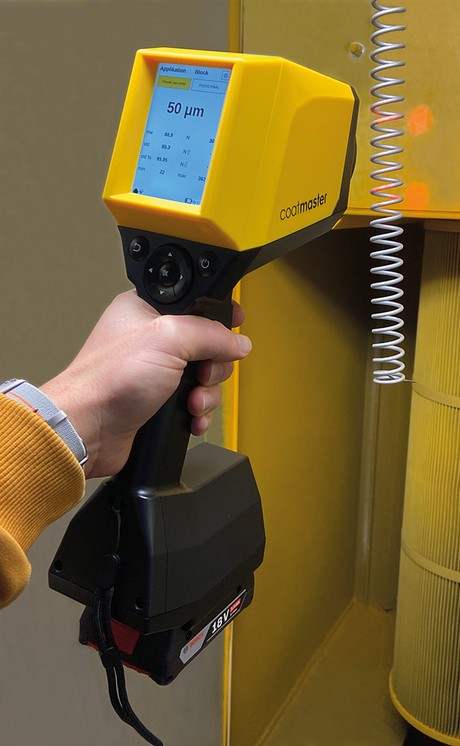
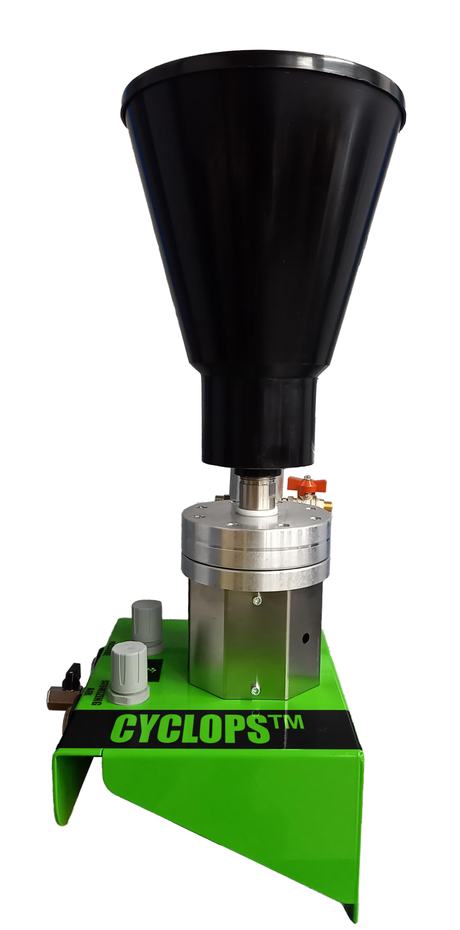
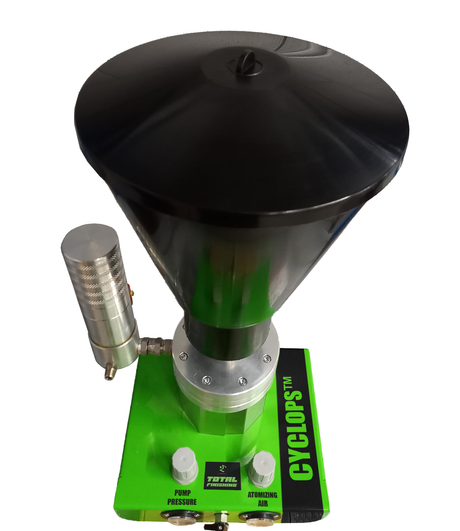
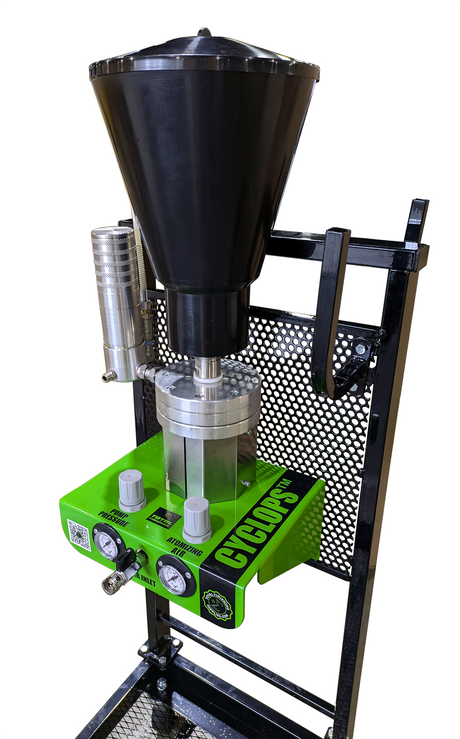
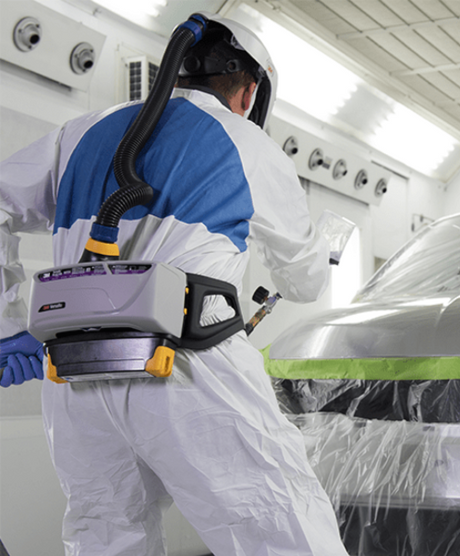
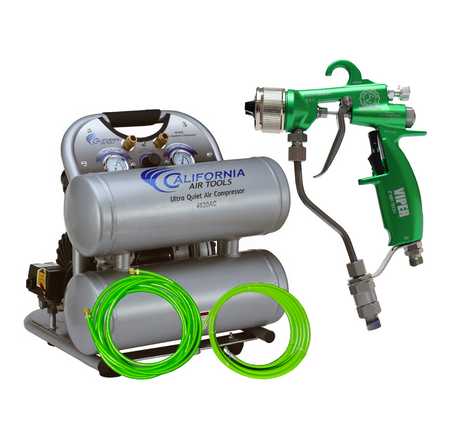
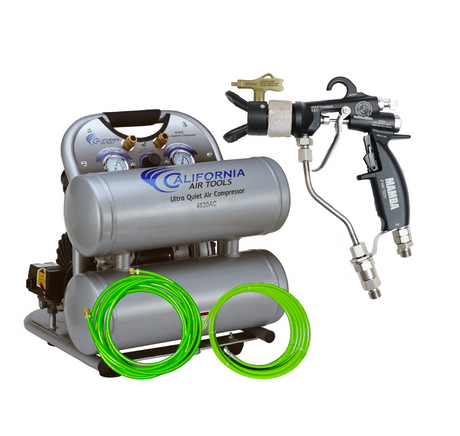
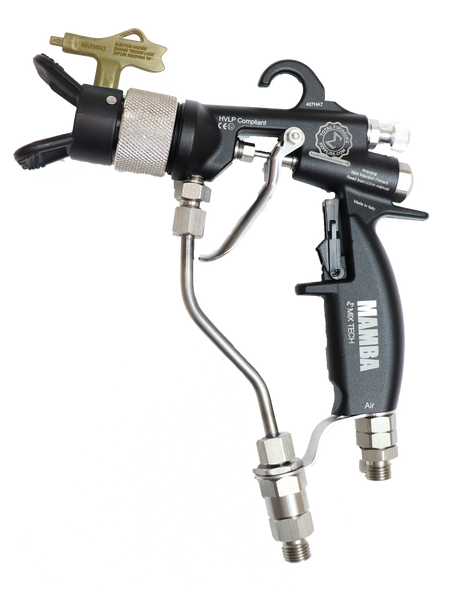
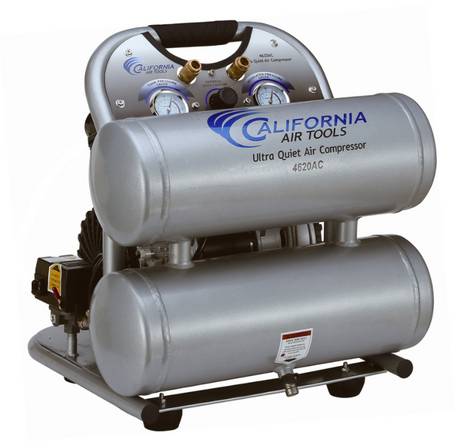
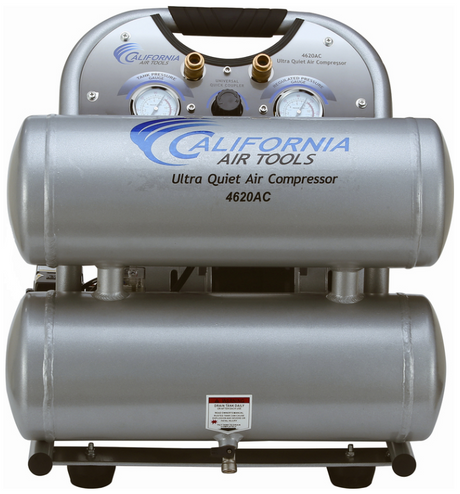
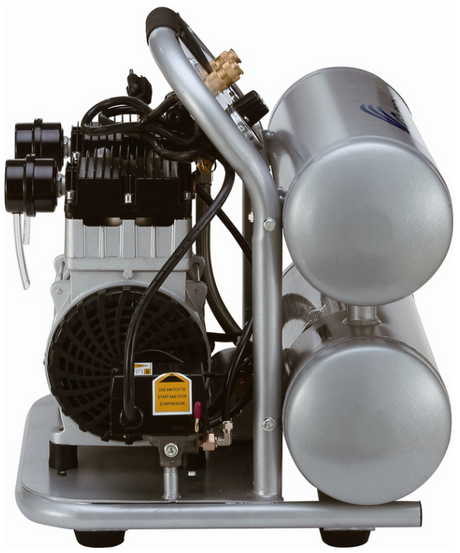
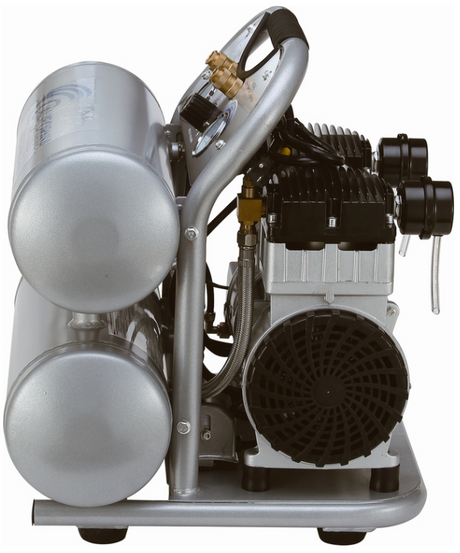
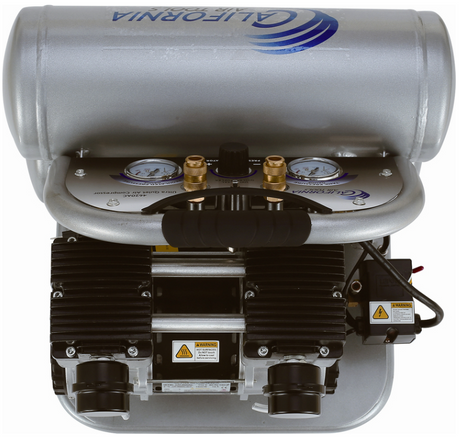
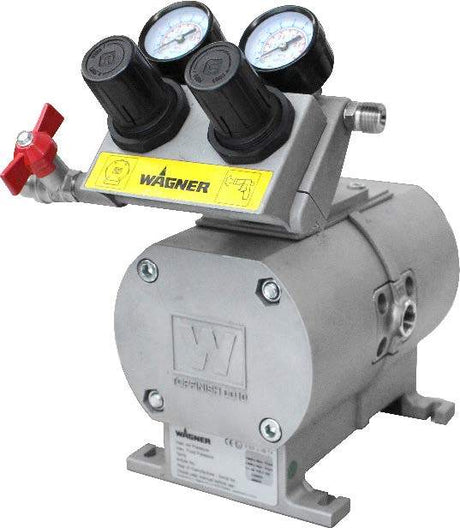
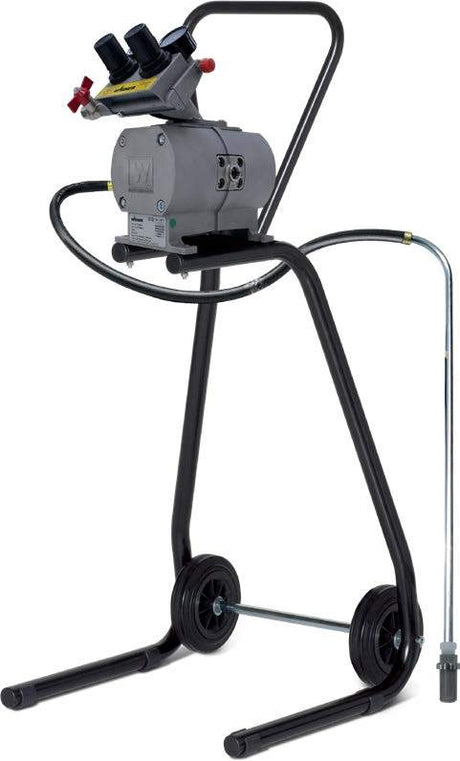
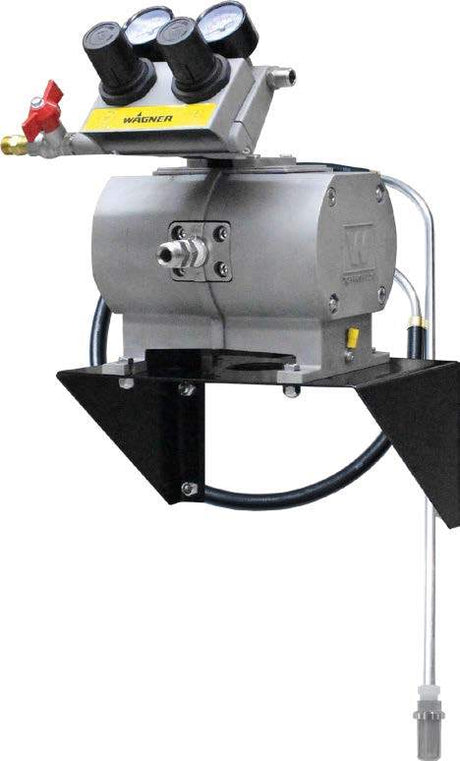
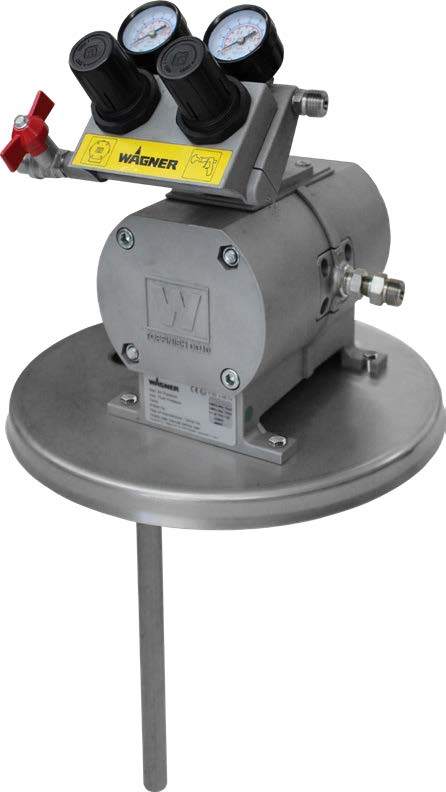
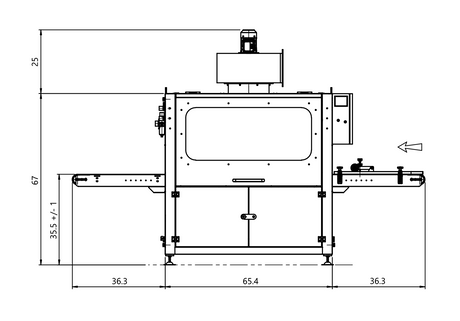
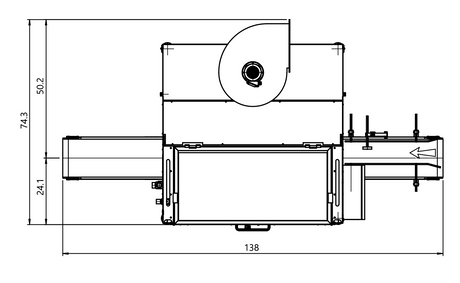
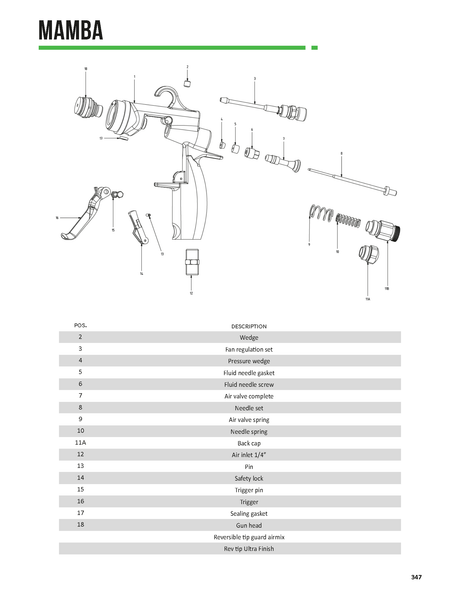
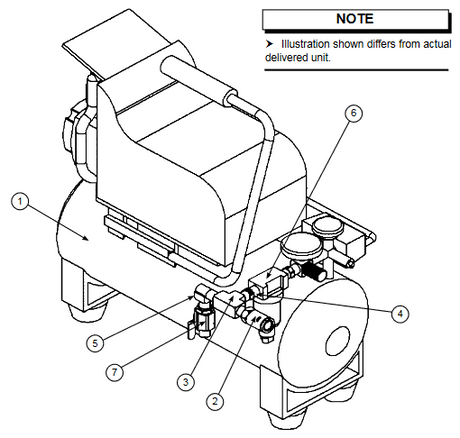
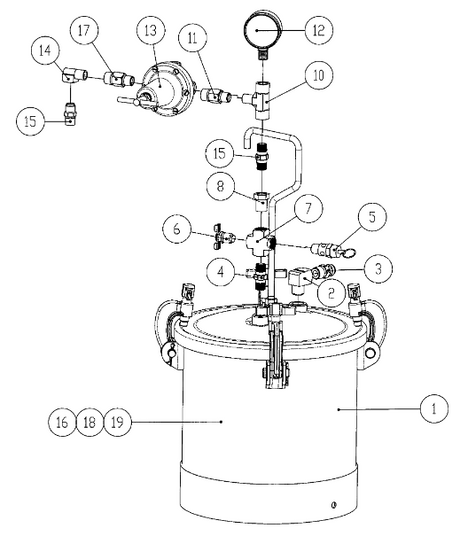
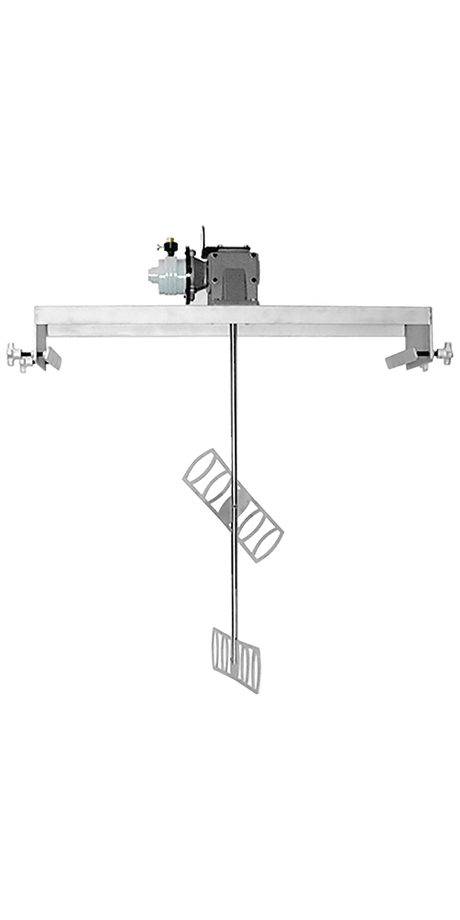
SATA air vision 5000: The Ultimate Respiratory Protection for Spray Booth Safety
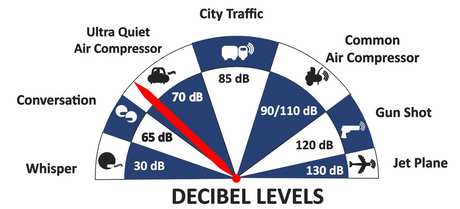
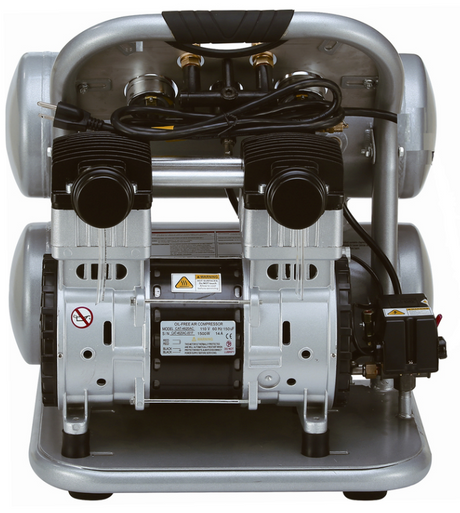
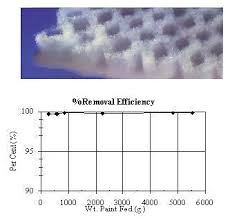
For professional painters, protecting your lungs in the spray booth is just as important as achieving a flawless finish. Harmful vapors like isocyanates and solvents are a real hazard—but the SATA...
Grace Aguilar |